Obsidian 使用技巧
¶1. quickadd + cmenu +templater + kanban 插件
学习资料视频:obsidian 无障碍联动效率插件 | 手把手打造高效双链个人知识库 | 全主观分享与推荐 | template | quickadd | cmenu
学习视频内嵌模式
- templater 用于设置文章模板
- quickadd + cmenu 用于生成
根据模板新建文章的快捷按钮 - kanban 用于根据 任务
- [ ]生成 看板 主要用于日常 todolist - 使用 taskList + checklist 追踪
#check任务 - calendar + daily note 日记
- banner 文章顶部背景
- Linter + YAML 模板头
- admonition 插件 用做 汇总查询 todolist 的背景部件 具体看
diaryTemplate模板 - Tasks插件的查询语法详情请看【效率办公】Obsidain插件之Tasks-任务管理利器
¶2. Dataview
¶1. Dataview 查询语法
1 | ```dataview |
学习资料:
-
List 查询
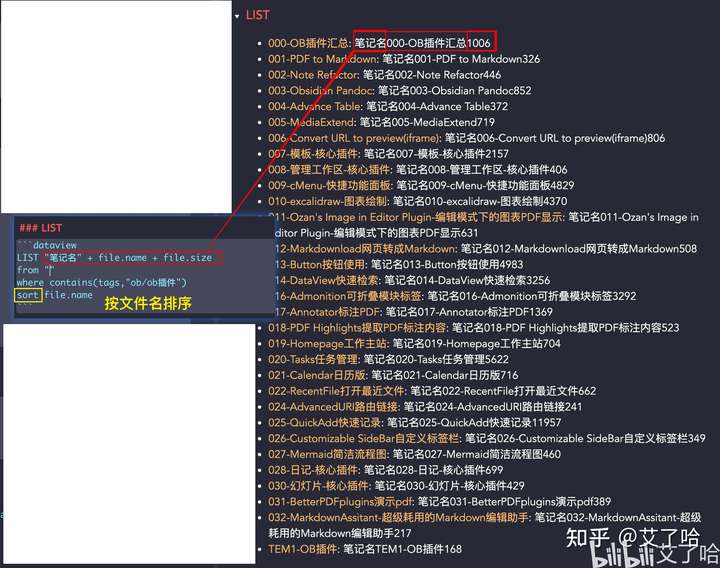
-
Table 查询
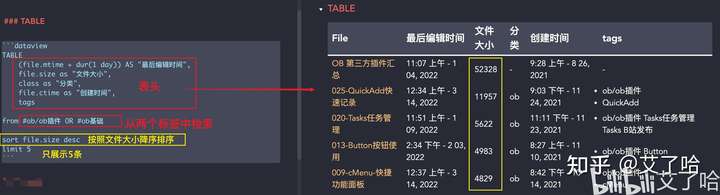
-
Task查询
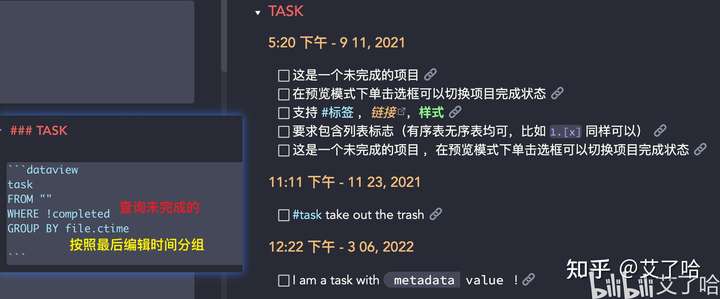
-
Calendar 查询
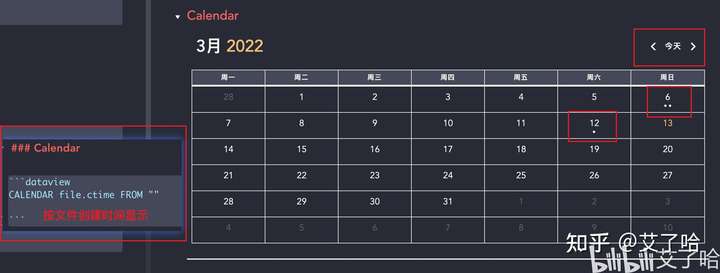
-
DataView 查询字段及命令


-
DataView 字段标识
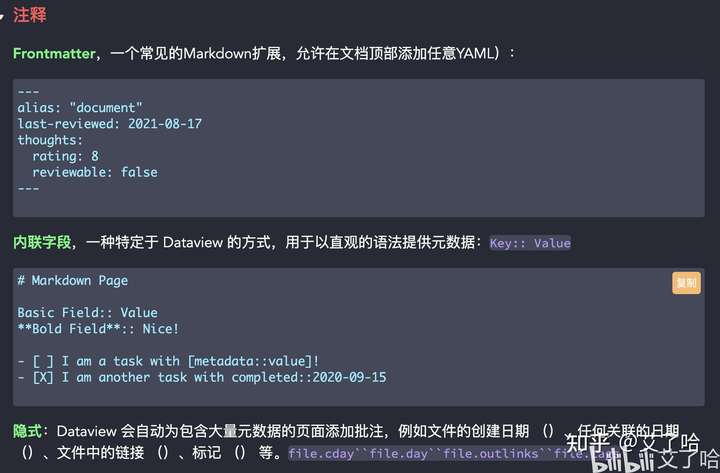
-
隐含字段
dataview能自动的对每个页面添加大量的元数据。
file.name: 该文件标题(字符串)。file.folder: 该文件所在的文件夹的路径(字符串)。file.path: 该文件的完整路径(字符串)。file.link: 该文件的一个链接(链接)。file.size: 该文件的大小(bytes)(数字)file.ctime: 该文件的创建日期(日期和时间)。file.cday: 该文件的创建日期(仅日期)。file.mtime: 该文件最后编辑日期(日期和时间)。file.mday: 该文件最后编辑日期(仅日期)。file.tags: 笔记中所有标签组成的数组。子标签按每个级别进行细分,所以#Tag/1/A将会在数组中储存为[#Tag, #Tag/1, #Tag/1/A]。file.etags: 笔记中所有显式标签组成的数组;不同于file.tags,不包含子标签。file.outlinks: 该文件所有外链(outgoing link)组成的数组。file.aliases: 笔记中所有别名组成的数组。
如果文件的标题内有一个日期(格式为yyyy-mm-dd或yyyymmdd),或者有一个Date字段/inline字段,它也有以下属性:file.day: 一个该文件的隐含日期。
¶2. Dataviewjs API
- 原始API
1 | /** A function which maps an array element to some value. */ |
- 代码块参考
1 |
|
- 查询例子:
1 | ```dataviewjs |